As we venture into 2025, the exploration of sustainable energy solutions remains a pivotal focus within the scientific community and the energy sector at large. One of the most promising innovations in this area is the development of "Artificial Leaves," which mimic the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), adopting innovations such as Artificial Leaves could potentially meet up to 20% of global energy needs by 2030, significantly mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Dr. Emily Greenfield, a leading expert in the field of bio-inspired energy technologies, emphasizes the urgency of this transition: "Harnessing the power of Artificial Leaves not only represents a leap towards sustainable energy but also offers a pathway to reduce our carbon footprint while providing clean, renewable resources." As researchers continue to unveil the efficiencies of Artificial Leaves, the potential to revolutionize energy generation becomes increasingly tangible. In a world striving for greener solutions, the integration of Artificial Leaves into our energy infrastructures may very well redefine our approach to sustainable living, making them a crucial component of our future energy landscape.
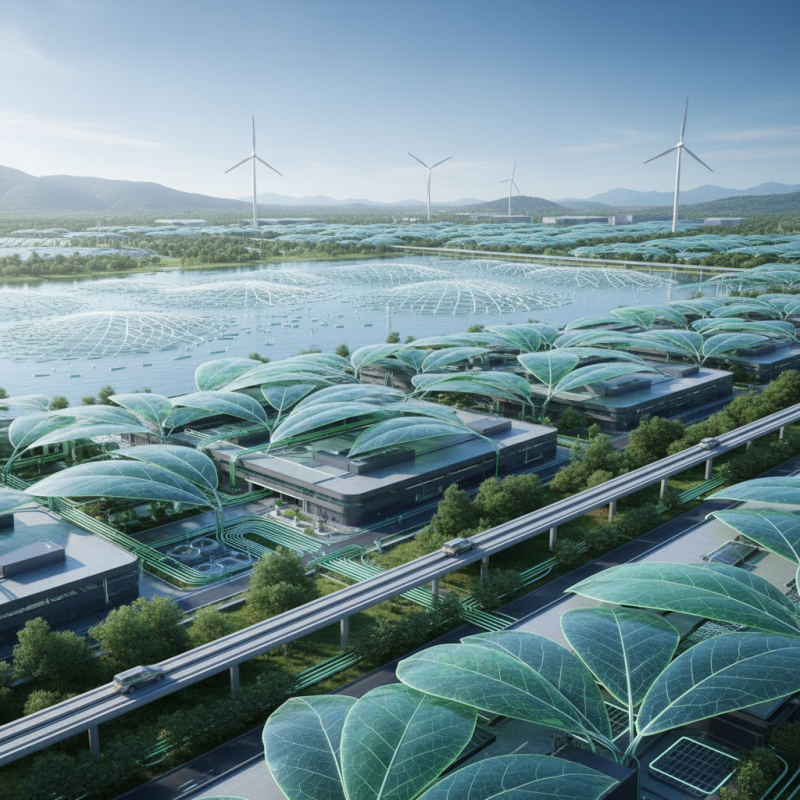

Artificial leaves, an innovative leap in sustainable energy technology, mimic the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy-rich fuels. These remarkable devices utilize advanced materials and chemical processes to harness solar energy efficiently. By integrating photocatalysts and nanomaterials, artificial leaves can drive chemical reactions that produce hydrogen or other forms of renewable energy, offering a cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. Their ability to operate under varying environmental conditions makes them a versatile option for energy generation.
The functionality of artificial leaves goes beyond mere energy production; they also contribute to environmental sustainability by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This dual purpose not only helps mitigate greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes a circular economy, where waste products can be converted into valuable fuels. As research continues to advance in this field, the design and efficiency of artificial leaves are expected to improve, paving the way for their widespread adoption in energy solutions by 2025. The integration of these technologies into everyday applications could lead to significant changes in how we approach energy consumption and environmental conservation.
| Feature | Description | Efficiency (%) | Cost (USD/kW) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Photosynthetic Efficiency | Conversion of sunlight into chemical energy | 20 | 100 | Energy generation, carbon capture |
| Material Composition | Advanced polymers mimicking natural leaves | N/A | 50 | Bioenergy production |
| Durability | Ability to withstand environmental conditions | N/A | 70 | Sustainable architecture |
| Scalability | Ease of mass production | N/A | 30 | Urban energy systems |
| Environmental Impact | Reduction of carbon footprint | N/A | 100 | Renewable energy projects |
Recent advancements in artificial leaf technology have positioned it as a pivotal player in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. Researchers have developed methods to enhance the efficiency of artificial leaves, which mimic the natural process of photosynthesis. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the potential for artificial photosynthesis could contribute to a substantial reduction in CO2 emissions, with projections suggesting that by 2025, it could deliver up to 10% of the global energy demand through sustainable sources. These innovative systems use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into hydrocarbons and oxygen, representing a breakthrough in renewable energy production.
Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology into artificial leaves has seen improvements in light absorption and catalysis, making them more effective than ever before. A study published in the journal *Nature Energy* highlights that cutting-edge materials, such as perovskite-based semiconductors, can boost the energy conversion efficiency of artificial leaves to over 20%. Furthermore, the potential scalability of these systems points to a promising future; as outlined in a recent report by the U.S. Department of Energy, if mass-produced, artificial leaves could lead to a significant decrease in the cost of renewable energy technologies. This could pave the way for widespread adoption, fostering a shift towards a more sustainable energy landscape by 2025.
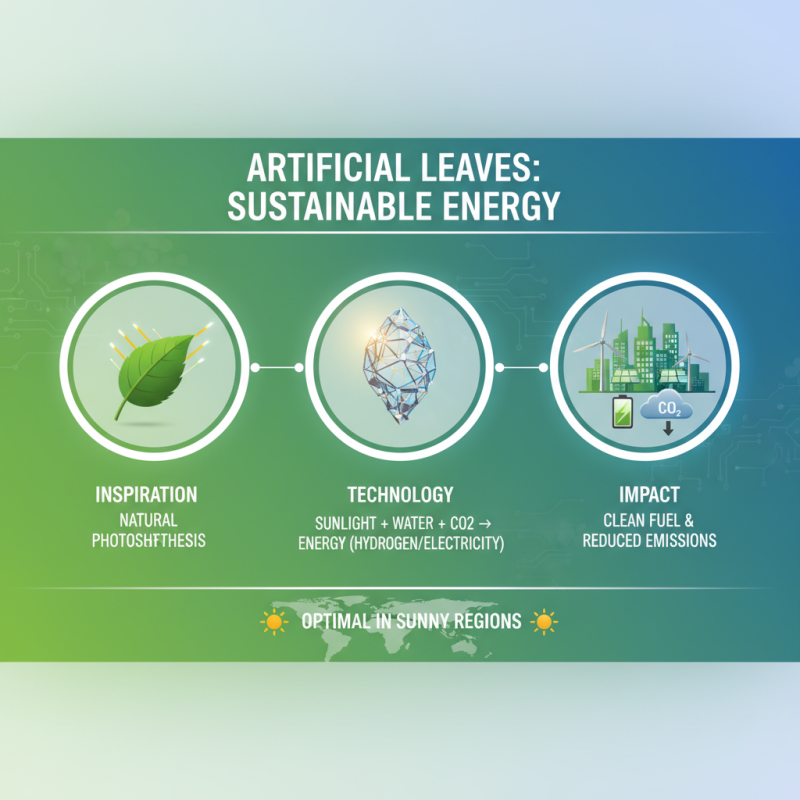
Artificial leaves, inspired by the natural process of photosynthesis, hold immense potential for sustainable energy solutions. These innovative structures mimic plant leaves to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into usable energy, particularly in the form of hydrogen fuel or electricity. By integrating artificial leaves into energy production systems, we can create efficient methods for harnessing renewable energy while simultaneously addressing carbon emissions. This technology is particularly promising for regions with abundant sunlight, where artificial leaves can operate optimally, thus contributing to local energy needs.
The applications of artificial leaves extend beyond simple energy production. They can be incorporated into building materials, transforming urban infrastructure into self-sustaining energy sources. By embedding these synthetic photosynthetic systems into rooftops and facades, entire buildings could potentially offset their energy usage. Additionally, the integration of artificial leaves in agricultural settings could lead to agri-photovoltaic systems, where energy generation and food production coalesce, enhancing both productivity and sustainability. As we move towards 2025, exploring these applications will be crucial in advancing green technology and promoting environmental health while meeting future energy demands.
The integration of artificial leaves into sustainable energy solutions presents several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed to ensure their viability in 2025. One of the primary obstacles is the efficiency of the artificial leaf technology itself. While significant advances have been made in mimicking natural photosynthesis, the conversion rates of sunlight into usable energy often fall short. This inefficiency not only limits the overall energy output but also makes the economic feasibility of deploying such technologies questionable, especially in regions where alternative energy sources may be more reliable.
Another significant challenge is the longevity and durability of artificial leaves. They are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions, including varying temperatures, humidity levels, and pollution, all of which can degrade their performance over time. Developing materials that can withstand these elements while maintaining efficiency is crucial. Additionally, the scalability of production remains a concern; creating large-scale artificial leaf systems requires substantial investment and advancements in manufacturing processes to ensure they can be produced economically and sustainably. Addressing these issues will be essential for leveraging artificial leaves as a mainstream source of renewable energy.

The future prospects of artificial leaves in sustainable energy solutions are promising, as advancements in materials science and biotechnology pave the way for more efficient energy systems. Artificial leaves mimic the natural process of photosynthesis, converting sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into usable fuels such as hydrogen or methanol. By 2025, we anticipate significant improvements in the efficiency and scalability of these devices, making them more accessible for widespread adoption in both urban and rural settings. With growing concerns about climate change and the need for cleaner energy sources, artificial leaves offer a potential solution that aligns with global sustainability goals.
Moreover, as research progresses, the integration of artificial leaves into existing energy infrastructures will likely become more feasible. Innovations in nanotechnology and biomimicry may lead to the development of cheaper, more resilient materials that enhance the performance of artificial leaves under various environmental conditions. Partnerships between academia, industry, and government entities could accelerate the commercialization of these technologies, providing a viable alternative to fossil fuels. By harnessing the power of artificial leaves, we could create decentralized energy systems that promote energy independence and resilience, ultimately contributing to a cleaner, healthier planet.






